A Method for Reconstructing 3D Skeleton of Coronary Artery from 2D X-ray Angiographic Images
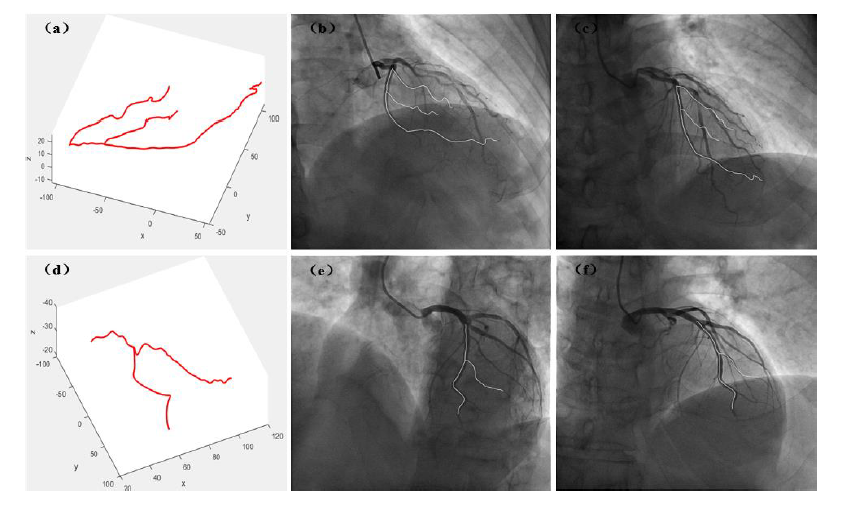
Abstract—X-ray angiographic imaging is commonly used for diagnosis and treatment planning of coronary artery disease. However, it is produced via perspective projection principle, causing two-dimensional (2D) views with vessel segments overlapping and shortening, which prevents physicians from observing the vascular structure clearly. Reconstructing a three-dimensional (3D) skeleton of coronary artery from 2D X-ray angiographic images is able to improve the accuracy and efficiency for diagnosis of coronary heart disease. Therefore, we propose a novel method to reconstruct the accurate 3D coronary artery skeletons from 2D X-ray angiographic images. Specifically, the 3D coronary artery skeleton is represented with a point-cloud, the impact of rigid motions including device and patient movement are both considered in our method. Additionally, an iterative correction method is introduced to refine the coarse reconstruction results. Evaluation with 10 cases of clinical data show that average reprojection error of our reconstructed models is 0.114 ± 0.051 mm, which is significantly reduced compared with that of related methods, and meets clinical requirements.