Patch-based adaptive background subtraction for vascular enhancement in x-ray cineangiograms
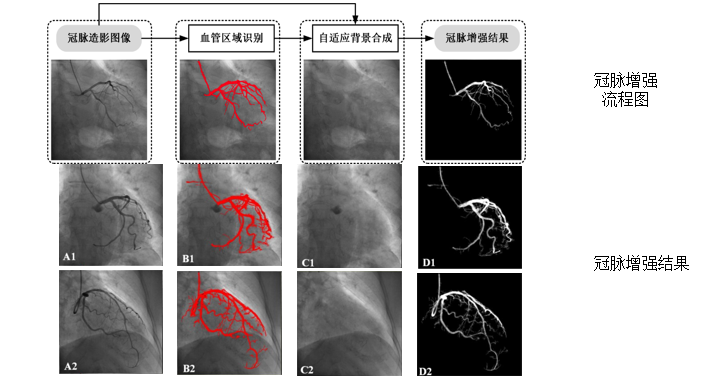
Abstract—Objective: Automatic vascular enhancement in X-ray cineangiography is of crucial interest, for instance, for better visualizing and quantifying coronary arteries in diagnostic and interventional procedures. Methods: A novel patch-based adaptive background subtraction method (PABSM) is proposed automatically enhancing vessels in coronary X-ray cineangiography. First, pixels in the cineangiogram are described by the vesselness and Gabor features. Second, a classifier is utilized to separate the cineangiogram into the rough vascular and non-vascular region. Dilation is applied to the classified binary image to include more vascular region. Third, a patch-based background synthesis is utilized to fill the removed vascular region. Results: A database containing 320 cineangiograms of 175 patients was collected, and then an interventional cardiologist annotated all vascular structures. The performance of PABSM is compared with six state-of-the-art vascular enhancement methods regarding the precision–recall curve and C-value. The area under the precision–recall curve is 0.7133, and the C-value is 0.9659. Conclusion: PABSM can automatically enhance the coronary artery in the cineangiograms. It preserves the integrity of vascular topological structures, particularly in complex vascular regions, and removes noise caused by the non-uniform gray-level distribution in the cineangiogram. Significance: PABSM can avoid the motion artifacts and it eases the subsequent vascular segmentation, which is crucial for the diagnosis and interventional procedures of coronary artery diseases.