Sparse deformation prediction using Markove Decision Processes (MDP) for non-rigid registration of MR image
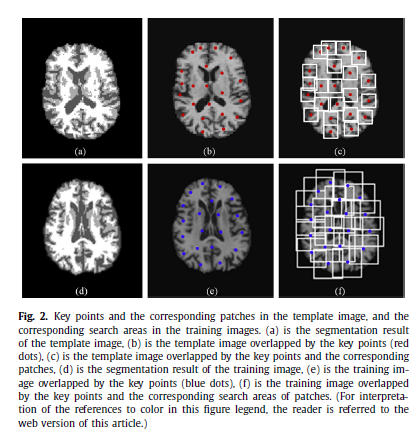
Abstract—Background and Objective.A framework of sparse deformation prediction using Markove Decision Processes is proposed for achieving a rapid and accurate registration by providing a suitable initial deformation.Methods.In the proposed framework, the tree is built based on the training set for each patch from the template image. The template patch is considered as the root. The node is the patch group in which multiple similar patches are extracted around a key point on the training image. Given the linkages between patch groups in the tree, MDP is introduced to select the optimal path with highest registration accuracy from each training patch to the template patch. The deformation between them is estimated along the selected path by patch-wise registration which can be realized by a non-learning-based method. Given the patches on a testing image, their best matching patches are fast chosen from the training patches and the corresponding deformations constitute a sparse deformation. A dense deformation for the entire test image is subsequently interpolated and used as an initial deformation for further registration.Results.With the non-learning-based registration as the baseline method, the proposed framework is evaluated using three datasets of inter-subject brain MR images with three learning-based methods. Experimental results of the non-learning-based method using the proposed framework reveal that the computation time is reduced by fivefold after using the proposed framework. And, with the same baseline method, the proposed framework demonstrates the higher accuracy than three learning-based methods which predicts the initial deformation at image scale. The mean Dice of three datasets for the tissues of the brain are 73.52%, 70.73% and 64.82%, respectively.Conclusions.The proposed framework rapidly registers the inter-subject brains and achieves the high mean Dice for the tissues of the brain.