Discriminative feature representation for noisy image quality assessment
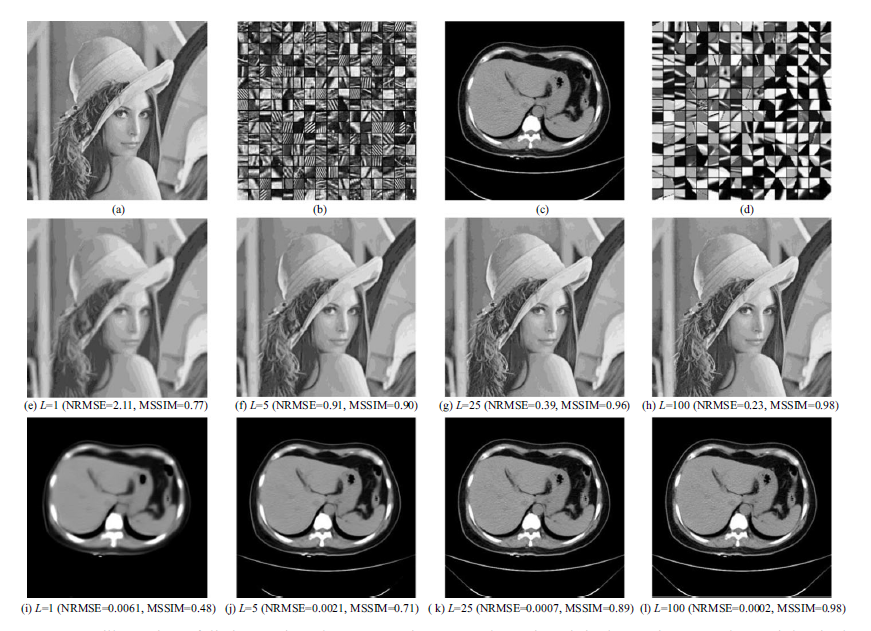
Abstract—Blind image quality assessment (BIQA) is one of the most challenging and difficult tasks in the field of IQA. Given that sparse representation through dictionary learning can learn the image feature well, this paper proposed a method termed Discriminative Feature Representation (DFR) from the perspective of feature learning for noise contaminated image quality assessment. DFR makes use of two sub-dictionaries composed of atoms featuring desirable image structures and undesirable noise, respectively. Noise is quantified via a joint evaluation of the sparse coefficients related to the atoms in the two subdictionaries. The method is validated using public databases with different types of noise, a comparison with other up-to-date methods is provided. The proposed method is also applied to CT images acquired at different-level doses and reconstructed by various wellknown algorithms.