Feasibility of augmented reality-guided transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
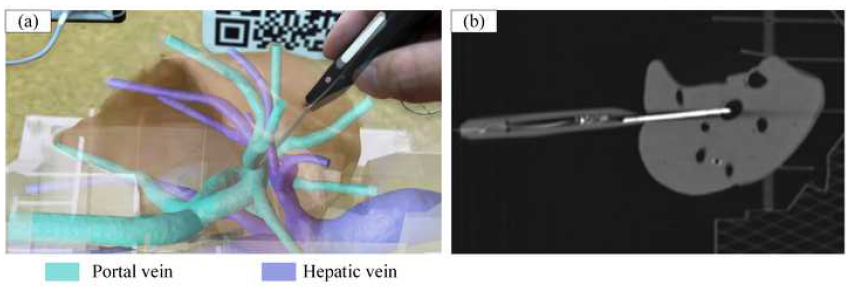
Abstract—Purpose: To investigate an augmented reality (AR)-guided endovascular puncture to facilitate successful transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS). Materials and Methods: An AR navigation system for TIPS was designed in this study. Three-dimensional (3D) liver models including portal and hepatic vein anatomy were extracted from preoperative computed tomography (CT) images. The 3D models, intraoperative subjects, and electromagnetic tracking information of the puncture needles were integrated through the system calibration. In the AR head-mounted display, the 3D models were overlaid on the subjects, which was a liver phantom in the first phase and live beagle dogs in the second phase. One life-size liver phantom and nine beagle dogs were used in the experiments. Post-puncture imaging was performed to validate whether the needle tip accessed the target hepatic vein successfully. Results: Endovascular punctures of the portal vein of the liver phantom were repeated 30 times under the guidance of the AR system, and the puncture needle successfully accessed the target vein during each attempt. In the experiments of live canine subjects, the punctures were successfully in 2 attempts in 7 beagle dogs and in 1 attempt in the remaining 2 dogs. Conclusion: The feasibility of AR-based navigation facilitating accurate and successful portal vein access in preclinical models of TIPS was validated.