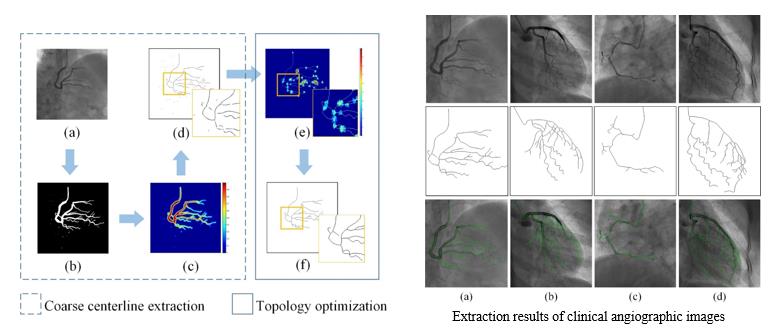
Topology optimization using multiple-possibility fusion for vasculature extraction
Abstract—Vascular centerline extraction from angiography images plays an important role in computer-aided diagnosis of vascular disease. To solve the common problems related to noise and inconsistent vasculatures from uneven perfusion, this paper proposes an automatic framework for accurate vascular centerline extraction from angiograms that uses multi-probability fusion-based topology optimization. In this framework, vascular region is first segmented using a learning-based method. Then, initial centerlines are obtained by applying iterative filtering operation and multi-direction indexed non-maximum suppression. Topology optimization is achieved by gap filling. A connection probability map is constructed utilizing the information of initial centerlines, texture, and orientation of vasculatures. Shortest path tracking is employed to search for optimal connections around gaps in the initial centerlines. The proposed framework is evaluated using simulative and clinical coronary angiographies. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can extract centerlines with F1 score of 97.28% ± 1.2% for vasculatures in 12 clinical angiographic images. It is evident that the proposed method can extract complete and accurate vascular centerlines from angiograms and can be used to repair gaps in other filamentary structures, such as roads and retinal blood vessels. This endows our method a great potential in the analysis of filamentary structures.